資料庫與 Doctrine ORM
螢幕錄影
您偏好影片教學嗎?請查看 Doctrine 螢幕錄影系列。
Symfony 提供了您在應用程式中使用資料庫所需的所有工具,這要歸功於 Doctrine,這是用於資料庫的最佳 PHP 函式庫集合。這些工具支援關聯式資料庫(如 MySQL 和 PostgreSQL)以及 NoSQL 資料庫(如 MongoDB)。
資料庫是一個廣泛的主題,因此文件分為三篇文章
- 本文說明在 Symfony 應用程式中使用關聯式資料庫的建議方式;
- 如果您需要低階存取以對關聯式資料庫執行原始 SQL 查詢(類似於 PHP 的 PDO),請閱讀另一篇文章;
- 如果您正在使用 MongoDB 資料庫,請閱讀 DoctrineMongoDBBundle 文件。
安裝 Doctrine
首先,透過 orm Symfony 套件以及 MakerBundle 安裝 Doctrine 支援,MakerBundle 將協助產生一些程式碼
1 2
$ composer require symfony/orm-pack
$ composer require --dev symfony/maker-bundle設定資料庫
資料庫連線資訊儲存為名為 DATABASE_URL 的環境變數。對於開發,您可以在 .env 內找到並自訂此變數
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
# .env (or override DATABASE_URL in .env.local to avoid committing your changes)
# customize this line!
DATABASE_URL="mysql://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:3306/db_name?serverVersion=8.0.37"
# to use mariadb:
# Before doctrine/dbal < 3.7
# DATABASE_URL="mysql://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:3306/db_name?serverVersion=mariadb-10.5.8"
# Since doctrine/dbal 3.7
# DATABASE_URL="mysql://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:3306/db_name?serverVersion=10.5.8-MariaDB"
# to use sqlite:
# DATABASE_URL="sqlite:///%kernel.project_dir%/var/app.db"
# to use postgresql:
# DATABASE_URL="postgresql://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:5432/db_name?serverVersion=12.19 (Debian 12.19-1.pgdg120+1)&charset=utf8"
# to use oracle:
# DATABASE_URL="oci8://db_user:db_password@127.0.0.1:1521/db_name"警告
如果使用者名稱、密碼、主機或資料庫名稱包含 URI 中視為特殊的任何字元(例如 : / ? # [ ] @ ! $ & ' ( ) * + , ; =),則必須對其進行編碼。請參閱 RFC 3986 以取得保留字元的完整清單。您可以使用 urlencode 函數對其進行編碼,或使用 urlencode 環境變數處理器。在這種情況下,您需要移除 config/packages/doctrine.yaml 中的 resolve: 前綴,以避免錯誤:url: '%env(DATABASE_URL)%'
現在您的連線參數已設定完成,Doctrine 可以為您建立 db_name 資料庫
1
$ php bin/console doctrine:database:createconfig/packages/doctrine.yaml 中還有更多選項可以設定,包括您的 server_version(例如,如果您使用 MySQL 8.0.37,則為 8.0.37),這可能會影響 Doctrine 的運作方式。
提示
還有許多其他 Doctrine 命令。執行 php bin/console list doctrine 以查看完整清單。
建立實體類別
假設您正在建置一個需要顯示產品的應用程式。甚至在考慮 Doctrine 或資料庫之前,您就已經知道您需要一個 Product 物件來表示這些產品。
您可以使用 make:entity 命令來建立此類別以及您需要的任何欄位。此命令會詢問您一些問題 - 像下面這樣回答它們
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
$ php bin/console make:entity
Class name of the entity to create or update:
> Product
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
> name
Field type (enter ? to see all types) [string]:
> string
Field length [255]:
> 255
Can this field be null in the database (nullable) (yes/no) [no]:
> no
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
> price
Field type (enter ? to see all types) [string]:
> integer
Can this field be null in the database (nullable) (yes/no) [no]:
> no
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
>
(press enter again to finish)哇!您現在有一個新的 src/Entity/Product.php 檔案
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
// src/Entity/Product.php
namespace App\Entity;
use App\Repository\ProductRepository;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
#[ORM\Entity(repositoryClass: ProductRepository::class)]
class Product
{
#[ORM\Id]
#[ORM\GeneratedValue]
#[ORM\Column]
private ?int $id = null;
#[ORM\Column(length: 255)]
private ?string $name = null;
#[ORM\Column]
private ?int $price = null;
public function getId(): ?int
{
return $this->id;
}
// ... getter and setter methods
}提示
從 MakerBundle 開始:v1.57.0 - 您可以將 --with-uuid 或 --with-ulid 傳遞至 make:entity。利用 Symfony 的 Uid Component,這會產生一個實體,其 id 類型為 Uuid 或 Ulid,而不是 int。
注意
從 v1.44.0 開始 - MakerBundle:僅支援使用 PHP 屬性的實體。
注意
對於價格是整數感到困惑嗎?別擔心:這只是一個範例。但是,將價格儲存為整數(例如 100 = 1 美元)可以避免四捨五入的問題。
警告
當在 MySQL 5.6 和更早版本中使用 InnoDB 表格時,索引鍵前綴有 767 位元組的限制。字串欄位的長度為 255 個字元且 utf8mb4 編碼會超過該限制。這表示任何類型為 string 且 unique=true 的欄位都必須將其最大 length 設定為 190。否則,您會看到此錯誤:"[PDOException] SQLSTATE[42000]: Syntax error or access violation: 1071 Specified key was too long; max key length is 767 bytes"。
此類別稱為「實體」。很快地,您就能夠將 Product 物件儲存到資料庫中的 product 表格並進行查詢。 Product 實體中的每個屬性都可以對應到該表格中的欄位。這通常使用屬性來完成:您在每個屬性上方看到的 #[ORM\Column(...)] 註解
make:entity 命令是一個讓生活更輕鬆的工具。但這是您的程式碼:新增/移除欄位、新增/移除方法或更新設定。
Doctrine 支援各種欄位類型,每種欄位類型都有自己的選項。請查看 Doctrine 文件中的 Doctrine 對應類型清單。如果您想要使用 XML 而不是屬性,請將 type: xml 和 dir: '%kernel.project_dir%/config/doctrine' 新增至 config/packages/doctrine.yaml 檔案中實體對應。
警告
請注意不要使用保留的 SQL 關鍵字作為表格或欄位名稱(例如 GROUP 或 USER)。請參閱 Doctrine 的 保留的 SQL 關鍵字文件,以了解如何逸出這些關鍵字。或者,使用類別上方的 #[ORM\Table(name: 'groups')] 變更表格名稱,或使用 name: 'group_name' 選項設定欄位名稱。
遷移:建立資料庫表格/結構描述
Product 類別已完全設定,可以儲存到 product 表格。如果您剛定義此類別,您的資料庫實際上還沒有 product 表格。若要新增它,您可以利用已安裝的 DoctrineMigrationsBundle
1
$ php bin/console make:migration提示
從 MakerBundle 開始:v1.56.0 - 將 --formatted 傳遞至 make:migration 會產生一個美觀整潔的遷移檔案。
如果一切正常,您應該會看到類似這樣的內容
1 2 3 4
SUCCESS!
Next: Review the new migration "migrations/Version20211116204726.php"
Then: Run the migration with php bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate如果您開啟此檔案,它會包含更新資料庫所需的 SQL!若要執行該 SQL,請執行您的遷移
1
$ php bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate此命令會執行所有尚未針對您的資料庫執行的遷移檔案。當您部署到正式環境時,您應該執行此命令以保持您的正式環境資料庫為最新狀態。
遷移 & 新增更多欄位
但是,如果您需要將新的欄位屬性新增至 Product,例如 description?您可以編輯類別以新增新的屬性。但是,您也可以再次使用 make:entity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
$ php bin/console make:entity
Class name of the entity to create or update
> Product
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
> description
Field type (enter ? to see all types) [string]:
> text
Can this field be null in the database (nullable) (yes/no) [no]:
> no
New property name (press <return> to stop adding fields):
>
(press enter again to finish)這會新增新的 description 屬性以及 getDescription() 和 setDescription() 方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
// src/Entity/Product.php
// ...
+ use Doctrine\DBAL\Types\Types;
class Product
{
// ...
+ #[ORM\Column(type: Types::TEXT)]
+ private string $description;
// getDescription() & setDescription() were also added
}新的屬性已對應,但它還不存在於 product 表格中。沒問題!產生新的遷移
1
$ php bin/console make:migration這次,產生檔案中的 SQL 看起來會像這樣
1
ALTER TABLE product ADD description LONGTEXT NOT NULL遷移系統非常聰明。它會將您的所有實體與資料庫的目前狀態進行比較,並產生同步它們所需的 SQL!和以前一樣,執行您的遷移
1
$ php bin/console doctrine:migrations:migrate警告
如果您使用的是 SQLite 資料庫,您會看到以下錯誤:PDOException: SQLSTATE[HY000]: General error: 1 Cannot add a NOT NULL column with default value NULL。將 nullable=true 選項新增至 description 屬性以修正問題。
這只會執行一個新的遷移檔案,因為 DoctrineMigrationsBundle 知道第一個遷移已經在稍早執行過了。在幕後,它會管理一個 migration_versions 表格來追蹤此資訊。
每次您變更結構描述時,請執行這兩個命令來產生遷移,然後執行它。請務必提交遷移檔案,並在部署時執行它們。
提示
如果您偏好手動新增新屬性,make:entity 命令可以為您產生 getter 和 setter 方法
1
$ php bin/console make:entity --regenerate如果您進行了一些變更並想要重新產生所有 getter/setter 方法,也請傳遞 --overwrite。
將物件持久化到資料庫
現在是時候將 Product 物件儲存到資料庫了!讓我們建立一個新的控制器來實驗
1
$ php bin/console make:controller ProductController在控制器內,您可以建立新的 Product 物件、在其上設定資料,並儲存它
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
// ...
use App\Entity\Product;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product', name: 'create_product')]
public function createProduct(EntityManagerInterface $entityManager): Response
{
$product = new Product();
$product->setName('Keyboard');
$product->setPrice(1999);
$product->setDescription('Ergonomic and stylish!');
// tell Doctrine you want to (eventually) save the Product (no queries yet)
$entityManager->persist($product);
// actually executes the queries (i.e. the INSERT query)
$entityManager->flush();
return new Response('Saved new product with id '.$product->getId());
}
}試試看!
恭喜!您剛在 product 表格中建立了您的第一個資料列。為了證明這一點,您可以直接查詢資料庫
1 2 3 4
$ php bin/console dbal:run-sql 'SELECT * FROM product'
# on Windows systems not using Powershell, run this command instead:
# php bin/console dbal:run-sql "SELECT * FROM product"更詳細地查看先前的範例
- 第 13 行
EntityManagerInterface $entityManager引數告訴 Symfony 將 Entity Manager 服務注入到控制器方法中。此物件負責將物件儲存到資料庫以及從資料庫提取物件。 - 第 15-18 行 在此區段中,您會像處理任何其他一般 PHP 物件一樣,實例化和處理
$product物件。 - 第 21 行
persist($product)呼叫告訴 Doctrine「管理」$product物件。這不會導致對資料庫進行查詢。 - 第 24 行 當呼叫
flush()方法時,Doctrine 會檢查它正在管理的所有物件,以查看它們是否需要持久化到資料庫。在此範例中,$product物件的資料在資料庫中不存在,因此實體管理員會執行INSERT查詢,在product表格中建立新的資料列。
注意
如果 flush() 呼叫失敗,則會擲回 Doctrine\ORM\ORMException 例外。請參閱 交易和並行。
無論您是建立或更新物件,工作流程始終相同:Doctrine 足夠聰明,可以知道它應該 INSERT 還是 UPDATE 您的實體。
驗證物件
Symfony 驗證器可以重複使用 Doctrine 元資料來執行一些基本驗證任務。首先,新增或設定 auto_mapping 選項,以定義 Symfony 應內省哪些實體以新增自動驗證約束。
考慮以下控制器程式碼
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Validator\ValidatorInterface;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product', name: 'create_product')]
public function createProduct(ValidatorInterface $validator): Response
{
$product = new Product();
// ... update the product data somehow (e.g. with a form) ...
$errors = $validator->validate($product);
if (count($errors) > 0) {
return new Response((string) $errors, 400);
}
// ...
}
}雖然 Product 實體未定義任何明確的 驗證設定,但如果 auto_mapping 選項將其包含在要內省的實體清單中,Symfony 將為其推斷一些驗證規則並套用它們。
例如,假設 name 屬性在資料庫中不能為 null,則會自動將 NotNull 約束新增至屬性(如果它尚未包含該約束)。
下表總結了 Doctrine 元資料與 Symfony 自動新增的對應驗證約束之間的對應關係
| Doctrine 屬性 | 驗證約束 | 注意事項 |
|---|---|---|
nullable=false |
NotNull | 需要安裝 PropertyInfo 组件 |
type |
Type | 需要安裝 PropertyInfo 组件 |
unique=true |
UniqueEntity | |
length |
Length |
由於 Form 组件 以及 API Platform 在內部使用 Validator 组件,因此您的所有表單和 Web API 也將自動受益於這些自動驗證約束。
此自動驗證是一項不錯的功能,可以提高您的生產力,但它並不能完全取代驗證設定。您仍然需要新增一些 驗證約束,以確保使用者提供的資料正確。
從資料庫提取物件
從資料庫中提取物件甚至更容易。假設您想要能夠前往 /product/1 以查看您的新產品
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/{id}', name: 'product_show')]
public function show(EntityManagerInterface $entityManager, int $id): Response
{
$product = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class)->find($id);
if (!$product) {
throw $this->createNotFoundException(
'No product found for id '.$id
);
}
return new Response('Check out this great product: '.$product->getName());
// or render a template
// in the template, print things with {{ product.name }}
// return $this->render('product/show.html.twig', ['product' => $product]);
}
}另一種可能性是使用 ProductRepository,方法是使用 Symfony 的自動裝配並由依賴注入容器注入
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use App\Repository\ProductRepository;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/{id}', name: 'product_show')]
public function show(ProductRepository $productRepository, int $id): Response
{
$product = $productRepository
->find($id);
// ...
}
}試試看!
當您查詢特定類型的物件時,您始終使用稱為其「repository」的物件。您可以將 repository 視為一個 PHP 類別,其唯一的工作是協助您提取特定類別的實體。
一旦您擁有 repository 物件,您就擁有許多輔助方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
$repository = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class);
// look for a single Product by its primary key (usually "id")
$product = $repository->find($id);
// look for a single Product by name
$product = $repository->findOneBy(['name' => 'Keyboard']);
// or find by name and price
$product = $repository->findOneBy([
'name' => 'Keyboard',
'price' => 1999,
]);
// look for multiple Product objects matching the name, ordered by price
$products = $repository->findBy(
['name' => 'Keyboard'],
['price' => 'ASC']
);
// look for *all* Product objects
$products = $repository->findAll();您也可以為更複雜的查詢新增自訂方法!稍後在資料庫與 Doctrine ORM 區段中會詳細介紹。
提示
在呈現 HTML 頁面時,頁面底部的 Web 偵錯工具列將顯示查詢次數和執行查詢所花費的時間
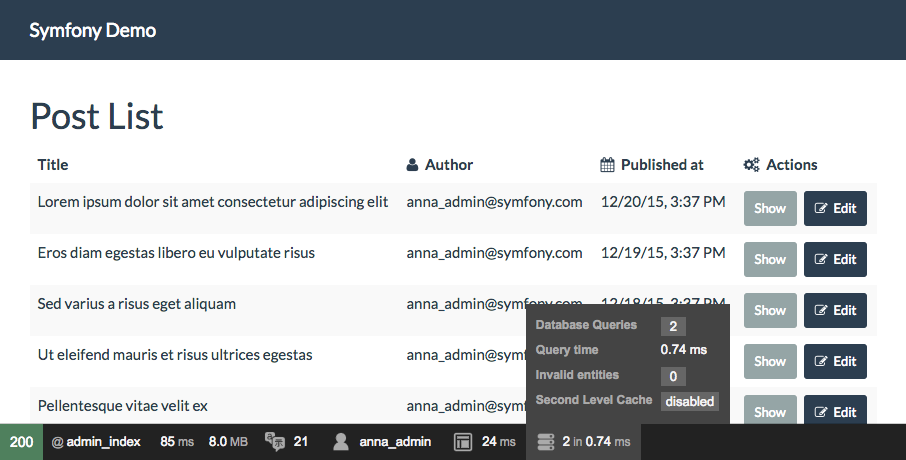
如果資料庫查詢次數過高,圖示會變成黃色,表示可能存在問題。按一下圖示以開啟 Symfony Profiler 並查看已執行的確切查詢。如果您沒有看到 Web 偵錯工具列,請執行此命令安裝 profiler Symfony 套件:composer require --dev symfony/profiler-pack。
如需更多資訊,請閱讀 Symfony profiler 文件。
自動提取物件 (EntityValueResolver)
2.7.1
DoctrineBundle 2.7.1 中引入了 EntityValueResolver 的自動裝配。
在許多情況下,您可以使用 EntityValueResolver 為您自動執行查詢!您可以將控制器簡化為
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use App\Repository\ProductRepository;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/{id}')]
public function show(Product $product): Response
{
// use the Product!
// ...
}
}就這樣!套件會使用路由中的 {id} 來依 id 欄位查詢 Product。如果找不到,則會產生 404 頁面。
提示
當全域啟用時,可以使用設定為 disabled 的 MapEntity 在特定控制器上停用此行為
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
public function show(
#[CurrentUser]
#[MapEntity(disabled: true)]
User $user
): Response {
// User is not resolved by the EntityValueResolver
// ...
}自動提取
如果您的路由萬用字元與實體上的屬性相符,則解析器會自動提取它們
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
/**
* Fetch via primary key because {id} is in the route.
*/
#[Route('/product/{id}')]
public function showByPk(Product $product): Response
{
}
/**
* Perform a findOneBy() where the slug property matches {slug}.
*/
#[Route('/product/{slug}')]
public function showBySlug(Product $product): Response
{
}自動提取在以下情況下運作
- 如果
{id}在您的路由中,則這會用於透過find()方法依主鍵提取。 - 解析器將嘗試透過使用路由中所有實際上是您實體屬性的萬用字元(非屬性會被忽略)來執行
findOneBy()提取。
預設情況下,所有控制器都啟用此行為。如果您願意,您可以將此功能限制為僅在名為 id 的路由萬用字元上運作,以依主鍵尋找實體。若要執行此操作,請將選項 doctrine.orm.controller_resolver.auto_mapping 設定為 false。
當 auto_mapping 停用時,您可以使用 MapEntity 屬性,為任何控制器引數明確設定對應。您甚至可以使用 MapEntity 選項 控制 EntityValueResolver 行為
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use Symfony\Bridge\Doctrine\Attribute\MapEntity;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/{slug}')]
public function show(
#[MapEntity(mapping: ['slug' => 'slug'])]
Product $product
): Response {
// use the Product!
// ...
}
}透過表達式提取
如果自動提取不適用於您的使用案例,您可以使用 ExpressionLanguage 组件 撰寫表達式
1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/product/{product_id}')]
public function show(
#[MapEntity(expr: 'repository.find(product_id)')]
Product $product
): Response {
}在表達式中,repository 變數將是您實體的 Repository 類別,而任何路由萬用字元(例如 {product_id})都可作為變數使用。
在表達式中呼叫的 repository 方法也可以傳回實體清單。在這種情況下,請更新控制器引數的類型
1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/posts_by/{author_id}')]
public function authorPosts(
#[MapEntity(class: Post::class, expr: 'repository.findBy({"author": author_id}, {}, 10)')]
iterable $posts
): Response {
}7.1
Symfony 7.1 中引入了實體清單的對應。
這也可以用來協助解決多個參數
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
#[Route('/product/{id}/comments/{comment_id}')]
public function show(
Product $product,
#[MapEntity(expr: 'repository.find(comment_id)')]
Comment $comment
): Response {
}在上面的範例中,$product 參數會自動處理,但 $comment 則使用屬性進行設定,因為它們無法同時遵循預設慣例。
如果您需要從請求中取得其他資訊來查詢資料庫,您也可以透過 request 變數在您的表達式中存取請求。假設您想要根據名為 sort 的查詢參數來取得產品的第一個或最後一個評論
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
#[Route('/product/{id}/comments')]
public function show(
Product $product,
#[MapEntity(expr: 'repository.findOneBy({"product": id}, {"createdAt": request.query.get("sort", "DESC")})')]
Comment $comment
): Response {
}MapEntity 選項
MapEntity 屬性上有許多選項可用於控制行為
id-
如果設定了
id選項並與路由參數匹配,則解析器將依主鍵尋找1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/product/{product_id}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(id: 'product_id')] Product $product ): Response { } mapping-
設定要與
findOneBy()方法一起使用的屬性和值:鍵是路由佔位符名稱,值是 Doctrine 屬性名稱1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
#[Route('/product/{category}/{slug}/comments/{comment_slug}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(mapping: ['category' => 'category', 'slug' => 'slug'])] Product $product, #[MapEntity(mapping: ['comment_slug' => 'slug'])] Comment $comment ): Response { } exclude-
設定應該在
findOneBy()方法中使用的屬性,方法是排除一個或多個屬性,以便不使用所有屬性1 2 3 4 5 6 7
#[Route('/product/{slug}/{date}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(exclude: ['date'])] Product $product, \DateTime $date ): Response { } stripNull- 如果為 true,則當使用
findOneBy()時,任何為null的值將不會用於查詢。 objectManager-
預設情況下,
EntityValueResolver使用預設物件管理器,但您可以設定此項1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/product/{id}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(objectManager: 'foo')] Product $product ): Response { } evictCache- 如果為 true,則強制 Doctrine 始終從資料庫而非快取中提取實體。
disabled- 如果為 true,則
EntityValueResolver將不會嘗試替換參數。 message-
當發生 NotFoundHttpException 時顯示的可選自訂訊息,但僅在開發環境中(您不會在生產環境中看到此訊息)
1 2 3 4 5 6
#[Route('/product/{product_id}')] public function show( #[MapEntity(id: 'product_id', message: 'The product does not exist')] Product $product ): Response { }
7.1
message 選項在 Symfony 7.1 中引入。
更新物件
從 Doctrine 取得物件後,您與它的互動方式與任何 PHP 模型相同
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31
// src/Controller/ProductController.php
namespace App\Controller;
use App\Entity\Product;
use App\Repository\ProductRepository;
use Doctrine\ORM\EntityManagerInterface;
use Symfony\Component\HttpFoundation\Response;
use Symfony\Component\Routing\Attribute\Route;
// ...
class ProductController extends AbstractController
{
#[Route('/product/edit/{id}', name: 'product_edit')]
public function update(EntityManagerInterface $entityManager, int $id): Response
{
$product = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class)->find($id);
if (!$product) {
throw $this->createNotFoundException(
'No product found for id '.$id
);
}
$product->setName('New product name!');
$entityManager->flush();
return $this->redirectToRoute('product_show', [
'id' => $product->getId()
]);
}
}使用 Doctrine 編輯現有產品包含三個步驟
- 從 Doctrine 取得物件;
- 修改物件;
- 在實體管理器上呼叫
flush()。
您可以呼叫 $entityManager->persist($product),但這不是必要的:Doctrine 已經在「監視」您的物件以進行變更。
刪除物件
刪除物件非常相似,但需要呼叫實體管理器的 remove() 方法
1 2
$entityManager->remove($product);
$entityManager->flush();正如您可能預期的那樣,remove() 方法通知 Doctrine 您想要從資料庫中移除給定的物件。DELETE 查詢實際上要到呼叫 flush() 方法後才會執行。
查詢物件:Repository
您已經看過儲存庫物件如何讓您在無需任何工作的情況下執行基本查詢
1 2 3
// from inside a controller
$repository = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class);
$product = $repository->find($id);但是,如果您需要更複雜的查詢該怎麼辦?當您使用 make:entity 產生您的實體時,命令也產生了一個 ProductRepository 類別
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
// src/Repository/ProductRepository.php
namespace App\Repository;
use App\Entity\Product;
use Doctrine\Bundle\DoctrineBundle\Repository\ServiceEntityRepository;
use Doctrine\Persistence\ManagerRegistry;
class ProductRepository extends ServiceEntityRepository
{
public function __construct(ManagerRegistry $registry)
{
parent::__construct($registry, Product::class);
}
}當您取得您的儲存庫時(即 ->getRepository(Product::class)),它實際上是這個物件的實例!這是因為在您的 Product 實體類別頂端產生的 repositoryClass 設定。
假設您想要查詢價格高於特定價格的所有 Product 物件。為此在您的儲存庫中新增一個新方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28
// src/Repository/ProductRepository.php
// ...
class ProductRepository extends ServiceEntityRepository
{
public function __construct(ManagerRegistry $registry)
{
parent::__construct($registry, Product::class);
}
/**
* @return Product[]
*/
public function findAllGreaterThanPrice(int $price): array
{
$entityManager = $this->getEntityManager();
$query = $entityManager->createQuery(
'SELECT p
FROM App\Entity\Product p
WHERE p.price > :price
ORDER BY p.price ASC'
)->setParameter('price', $price);
// returns an array of Product objects
return $query->getResult();
}
}傳遞給 createQuery() 的字串可能看起來像 SQL,但它是 Doctrine Query Language。這讓您可以使用常用的查詢語言來輸入查詢,但參考的是 PHP 物件(即在 FROM 陳述式中)。
現在,您可以在儲存庫上呼叫此方法
1 2 3 4 5 6
// from inside a controller
$minPrice = 1000;
$products = $entityManager->getRepository(Product::class)->findAllGreaterThanPrice($minPrice);
// ...請參閱 服務容器,了解如何將儲存庫注入到任何服務中。
使用 Query Builder 查詢
Doctrine 還提供了 Query Builder,這是一種物件導向的查詢撰寫方式。當查詢是動態建構時(即基於 PHP 條件),建議使用此方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
// src/Repository/ProductRepository.php
// ...
class ProductRepository extends ServiceEntityRepository
{
public function findAllGreaterThanPrice(int $price, bool $includeUnavailableProducts = false): array
{
// automatically knows to select Products
// the "p" is an alias you'll use in the rest of the query
$qb = $this->createQueryBuilder('p')
->where('p.price > :price')
->setParameter('price', $price)
->orderBy('p.price', 'ASC');
if (!$includeUnavailableProducts) {
$qb->andWhere('p.available = TRUE');
}
$query = $qb->getQuery();
return $query->execute();
// to get just one result:
// $product = $query->setMaxResults(1)->getOneOrNullResult();
}
}使用 SQL 查詢
此外,如果需要,您可以使用 SQL 直接查詢
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
// src/Repository/ProductRepository.php
// ...
class ProductRepository extends ServiceEntityRepository
{
public function findAllGreaterThanPrice(int $price): array
{
$conn = $this->getEntityManager()->getConnection();
$sql = '
SELECT * FROM product p
WHERE p.price > :price
ORDER BY p.price ASC
';
$resultSet = $conn->executeQuery($sql, ['price' => $price]);
// returns an array of arrays (i.e. a raw data set)
return $resultSet->fetchAllAssociative();
}
}使用 SQL,您將取回原始資料,而不是物件(除非您使用 NativeQuery 功能)。
設定
請參閱 Doctrine 設定參考。
關聯與關聯性
Doctrine 提供了管理資料庫關係(也稱為關聯)所需的所有功能,包括 ManyToOne、OneToMany、OneToOne 和 ManyToMany 關係。
如需資訊,請參閱 如何使用 Doctrine 關聯 / 關係。
資料庫測試
閱讀關於 測試與資料庫互動的程式碼 的文章。
Doctrine 擴充套件 (Timestampable, Translatable 等)
Doctrine 社群建立了一些擴充功能來實作常見需求,例如「在建立實體時自動設定 createdAt 屬性的值」。請閱讀更多關於 可用的 Doctrine 擴充功能,並使用 StofDoctrineExtensionsBundle 將它們整合到您的應用程式中。